Image Formation by Lens
Image Formation by Lens: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Position of Image in Concave lens, Magnification in Convex Lens,Ray Diagrams in Convex Lens and Ray Diagrams in Concave Lens etc.
Important Questions on Image Formation by Lens
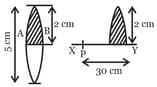
A converging lens of focal length 20 cm and diameter 5 cm is cut along the line AB. The part of the lens shown shaded in the diagram is now used to form an image of a point P placed 30 cm away from it on the line XY. Which is perpendicular to the plane of the lens. The image of P will be formed.
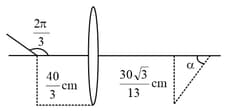
A rod of length makes an angle with the principal axis of a thin convex lens. The lens has a focal length of and is placed at a distance of from the object as shown in the figure. The height of the image is and the angle made by it with respect to the principal axis is $\alpha$ rad. The value of is , where is
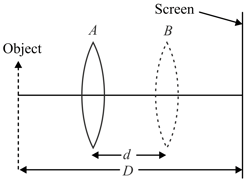
An illuminated object is placed at a distance from a screen. A convex lens of focal length is placed between them. A real image of the object is formed on the screen for two conjugate positions and of the lens separated by a distance . The respective linear magnifications of the image are and for positions and of the lens. Then
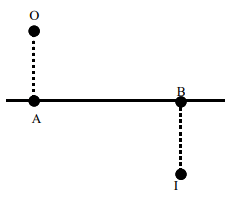
A luminous point object is placed at (real object), whose image is formed at as shown in the figure. Line is the optical axis. Which of the following statement is/are CORRECT ?
A glass slab has a concave surface of radius of curvature . The glass refractive index of . If a point object is placed on axis in air at a distance of from the concave face, find the position and nature of the image.
Describe the nature of the image formed by the concave lens when the object is kept at infinity while using the lens formula.
Draw the ray diagram of the formation of the image of an object which is kept at infinity from a concave lens using various sets of rays.
Explain the magnification when an object is placed between and of a convex lens.
Explain the nature of the image formed by a convex lens when the object is placed beyond the centre of curvature ().
Draw the ray diagram of the formation of the image of an object which is kept at infinity from the convex lens using various sets of rays.
The image of an object which is kept at focus of a convex lens is formed at infinity.
The image of an object of height in a thin lens has a height of and is erect. The image lies in front of the object at a distance of from it. The focal length of the lens is
The sun subtends an angle of when seen from the Earth. If the image of the sun is formed with a convex lens of focal length , what will be the approximate diameter of the image of the sun?
A thin cylindrical parallel light beam of beam diameter and intensity falls on a convex lens parallel to the principal axis symmetrically. The refracted light from the lens is obtained on the screen, which is perpendicular to the principal axis. Intensity obtained on the screen is for two positions of the screen, separated by a displacement of . What is the focal length of the lens in ? (Assume all the light to be transmitted from the lens)
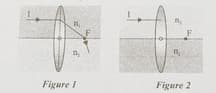
A convex lens in placed in two medium whose refractive indices are and . Figure 1 show how the incident ray I undergoes its path changes as per the setup. Which of the following option clearly completes the path of ray I in the second setup as shown in figure 2?
Which one of the following forms a virtual and erect image for all positions of the object?
Draw ray diagram to show the formation of image of an object which is kept at infinity from concave lens.
Magnification of a concave lens is
When the object is placed at focus of the concave lens, image is formed at _____.
What type of image is formed by concave lens ?
